- info@eltech.in
- +91-98204 88050
Static eliminators are used to eliminate static and dust. Static electricity is a problem, which companies face globally. It primarily affects industries, which handle non conductive materials like plastics, paper, board, laminates and textiles. The electrostatics attraction repulsion causes materials to stick to machinery, or to each other, leading to jams, slow machine speed and poor quality and productivity. Friction, pressure and separation are the major causes of static electricity. When humidity is lower, higher static charges are generated. It becomes more noticeable in the months of winter, in dry laminates, and in air conditioned environments. Use of our superior quality neutralized static eliminator ensures solution of all these problems and results in trouble free operation, increased profits and maximum customer satisfaction.
The main causes of static electricity are:
Contact & Separation between two materials – including friction, travelling over rollers etc. Rapid heat change e.g. material going through an oven, or polymers during injection moulding. High energy radiation, UV, X-ray, intense electric fields.Cutting action e.g on slitter-rewinders, sheet cutters, machining of plastics. Induction – standing in the electric field generated by a static charge or handling charged products and materials. Contact and separation is probably the most common cause of static in industry where film and sheet are being processed. It happens when material unwinds or passes over a roller. When the material touches the roller a small charge flows from the material to the roller causing an imbalance. As the material leaves the roller the voltage is magnified like the separating plates of a capacitor. The size of the resultant voltage is limited in practice by the breakdown strength of the surrounding materials, surface conduction etc. You often hear small cracks, or static discharges, as the material leaves the roller. This is where the static has reached the breakdown strength of the surrounding air. The plastic film is neutral before the roller, but as the film separates from the roller electrons flow onto the film giving it a negative charge. The remaining positive charge on the roller will disappear quickly if it is an earthed metal roller.
The surface layer of an electrically insulating material like plastic, paper or synthetic textile is usually not electrically charged. However, the material can become electrically charged under the following circumstances:
Friction when the surface of a material is rubbed against a material of the same or different kind.
Pressure when the material is run through two rollers.
Separation unwrapping of plastic foil from a roll.
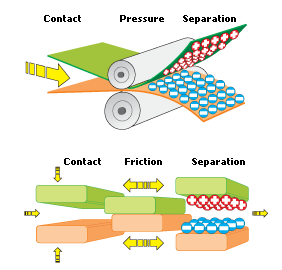
These processes are examples of handling that can result in an imbalance in the material’s electric charge. One surface becomes positively charged, the other one negatively. Because the material is electrically insulating, the charge cannot be conducted away through the material itself and the charge is now said to be static. The characteristics of electric charges to attract charges with opposite polarity or to repel those with identical polarity can cause immense problems during production.
Some materials cause or create more static electricity than others. Since static electricity is the collection of electrically charged particles on the surface of a material, various materials have a tendency of either giving up electrons and becoming positive (+) in charge or attracting electrons and becoming negative (−) in charge.
The Triboelectric Series is a list of materials, showing which have a greater tendency to become positive (+) and which have a greater tendency to become negative (−). The list is a handy tool to determine which combinations of materials create the most static electricity.
It can be seen that some objects easily acquire a positive charge, while others easily acquire a negative charge, depending upon the material of the object. Also, if objects consisting of materials located at greatly differing parts of the table shown at left touch each other, the amount of static electricity will become large.
For example, if static electricity is generated by copper and rubber for the reason indicated in the figure below, the copper will acquire a positive charge, and the rubber will acquire a negative charge.
The charging electric potential acquired by the human body and fluororesin is larger than that acquired by copper and rubber.

Every industry where non-conductive materials are used can be affected by static electricity.
In Particular: